Introduction to Achel Yaffe and Liver Cancer
Liver cancer has emerged as a significant health concern in recent years, with increasing prevalence alarming both medical professionals and patients alike. Among those affected by this disease is Achel Yaffe, whose personal battle with liver cancer not only highlights the struggles faced by those diagnosed but also serves as a catalyst for raising awareness about this worrisome condition. Achel’s story emphasizes the critical need for discussions surrounding liver cancer, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Liver cancer, classified primarily into hepatocellular carcinoma, accounts for the majority of cases and typically arises in individuals with chronic liver diseases such as cirrhosis or hepatitis B and C infections. As the global health landscape evolves, the rise of liver cancer can be attributed to several factors, including an increase in liver disease prevalence, changes in lifestyle, and environmental influences. With growing numbers, understanding the implications of liver cancer becomes paramount, particularly in addressing early detection and timely interventions.
Achel Yaffe’s circumstances underscore the importance of not only individual stories but also the wider implications they entail for liver cancer awareness and research fundraising efforts. His narrative serves to inform others about the reality of this condition, highlighting the urgency of educational outreach and access to medical resources. Indeed, the journey faced by Achel Yaffe is emblematic of numerous patients navigating the complexities of liver cancer. It urges us to delve deeper into understanding this ailment, urging healthcare providers and the general public to foster discussions about prevention, promotion of healthy lifestyles, and advancements in cancer research.
Types of Liver Cancer: A Comprehensive Overview
Liver cancer primarily consists of two categories: primary liver cancer and secondary liver cancer. Primary liver cancer originates in the liver cells and is categorized chiefly into hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which accounts for approximately 75% of all liver cancer cases. HCC arises from hepatocytes, the main functional cells of the liver. Secondary liver cancer, on the other hand, occurs when cancer cells from other parts of the body metastasize to the liver. The most common sources of secondary liver cancer include colorectal, breast, and lung cancers.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is significantly influenced by underlying liver diseases. Chronic viral infections, particularly those caused by the hepatitis B and C viruses, are major risk factors for developing HCC. Besides viral infections, conditions such as cirrhosis (often resulting from alcohol use or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease) also elevate the risk of liver cancer. Furthermore, certain genetic disorders, like hemochromatosis, can predispose individuals to liver complications, culminating in an increased cancer risk.
Regarding prevalence, liver cancer ranks as the sixth most common cancer globally and is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths, particularly in regions such as East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. Demographic factors also play a crucial role; for instance, HCC prevalence is notably higher among men compared to women, with rates varying significantly across different age groups. In regions where hepatitis infections are widespread, the incidence of liver cancer is particularly elevated. Understanding these distinctions and risk factors is crucial for both prevention and early detection of liver cancer, emphasizing the importance of regular screenings, especially for individuals at higher risk.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer often presents with several key symptoms that warrant immediate medical attention. Among the most prevalent symptoms are unexplained weight loss, jaundice, and persistent abdominal pain. Unexplained weight loss can occur even in the absence of dietary changes, often prompting individuals to seek out medical assistance. Jaundice, characterized by a yellowing of the skin and eyes, occurs due to the liver’s inability to process bilirubin effectively. This symptom can be accompanied by dark urine and pale stools. Abdominal pain, typically located in the upper right quadrant, may manifest as a dull ache or a more intense discomfort, which could signal the presence of tumors or liver enlargement.
Recognizing these symptoms early on is crucial, as timely diagnosis can significantly impact treatment outcomes. Screening for liver cancer is especially important for individuals in high-risk categories, including those with chronic liver disease, hepatitis infections, or a family history of liver-related conditions. Diagnostic methods utilized to confirm the presence of liver cancer comprise various imaging techniques and biopsies. Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are routinely employed to visualize anomalies in the liver structure. These non-invasive tools help in detecting tumors and assessing their size and spread.
If imaging tests suggest the possibility of liver cancer, a liver biopsy may be conducted to obtain a definitive diagnosis. A biopsy involves extracting a small sample of liver tissue for examination, allowing pathologists to identify cancerous cells microscopically. Incorporating regular screenings, particularly for at-risk groups, enhances the likelihood of early liver cancer detection and can significantly improve management and treatment options for affected individuals. Awareness of symptoms and appropriate diagnostic strategies serves as a vital element in combating this challenging disease.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Liver cancer, specifically Achel Yaffe liver cancer, is associated with a variety of risk factors that can significantly affect an individual’s likelihood of developing this serious condition. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for early detection and prevention. Among the primary risk factors are chronic infections with hepatitis B and C viruses. These viral infections can lead to liver inflammation, cirrhosis, and ultimately increase the risk of liver cancer. It is essential for individuals at increased risk to undergo regular screenings to monitor liver health.
Another notable risk factor linked to Achel Yaffe liver cancer is excessive alcohol consumption. Chronic alcoholism can result in liver damage and scarring, conditions that are closely related to the development of liver tumors. Limiting alcohol intake or abstaining from alcohol altogether can significantly reduce the risk of liver cancer. Furthermore, obesity and metabolic syndrome are emerging risk factors for liver disease. Obesity contributes to fatty liver disease, which is a precursor to both cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (the most common form of liver cancer). Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can play a vital role in liver health.
To mitigate these risks, individuals can adopt several preventive strategies. Vaccination against hepatitis B is available and can effectively reduce the incidence of the virus. Additionally, individuals should practice safe sex and avoid sharing needles to prevent hepatitis C transmission. Regular exercise, a nutrient-rich diet, and weight management are also fundamental lifestyle changes that can bolster liver health. By taking an active approach, individuals can significantly decrease their risk of developing Achel Yaffe liver cancer and promote overall well-being.
Treatment Options for Liver Cancer: A Closer Look
Treatment options for liver cancer, particularly Achel Yaffe liver cancer, are diverse and tailored to the individual patient’s health status, the tumor’s characteristics, and the cancer stage. Understanding these treatment modalities is fundamental for effective management of the disease. Surgical interventions are often the most effective approach when the cancer is diagnosed in its early stages.
Liver resection, which involves the surgical removal of a portion of the liver, is considered for patients whose tumors are localized and whose liver function remains intact. This surgery may offer a chance for cure, but its suitability must be carefully assessed based on the size, number, and location of the tumors, as well as the overall health of the liver. In cases where the cancer has affected a larger portion of the liver or if there are multiple tumors, liver transplantation becomes a viable option. This procedure not only removes the cancerous tissue but also addresses underlying liver disease, offering patients a better long-term outcome.
In addition to surgical treatments, nonsurgical options have gained traction, particularly for patients who may not be candidates for surgery or who have advanced liver cancer. Targeted therapy involves the use of drugs that specifically attack cancer cells without affecting normal cells, minimizing side effects. This approach targets specific pathways and mutations responsible for the growth of cancer cells. Similarly, immunotherapy leverages the body’s immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer cells, providing another line of defense against liver cancer.
It is essential for treatment plans to be personalized, considering not only the nature of the cancer but also the patient’s overall health, preferences, and treatment goals. Collaboration among a multidisciplinary team, including oncologists, surgeons, and liver specialists, ensures a comprehensive strategy tailored to achieve the best possible outcomes for individuals diagnosed with liver cancer.
Achel Yaffe’s Journey: Insights and Lessons Learned
Achel Yaffe’s battle with liver cancer serves as a poignant reminder of the challenges many individuals face in the fight against this devastating disease. Initially diagnosed at a time when he felt healthy, the sudden shift in his life required immediate adaptability. The diagnosis brought forth a myriad of emotions—fear, confusion, and a sense of urgency. Achel soon learned that the journey through cancer is often fraught with unexpected twists.
One of the foremost challenges Achel encountered was navigating the complexities of treatment options. With a diagnosis of liver cancer, the choices between surgery, chemotherapy, and newer targeted therapies required extensive research and consultations with specialists. He emphasized the importance of seeking multiple opinions to make informed decisions, a lesson that underscores the significance of patient advocacy in cancer care. Achel found himself grappling with questions about each treatment’s potential side effects and outcomes, which highlighted the need for comprehensive education on liver cancer.
Support systems played a crucial role throughout Achel’s journey, as he leaned on family, friends, and cancer support groups. Their emotional support was invaluable, providing him with a safe space to express his fears and anxieties. Achel also discovered the therapeutic effects of sharing his experiences with others undergoing similar challenges. These connections fostered a sense of community and camaraderie, encouraging him to remain resilient despite the difficult circumstances.
In addition to personal coping strategies, Achel has taken to advocating for liver cancer awareness. Understanding the signs and symptoms is vital for early detection, and he has engaged in campaigns to educate others about the disease. His journey is a testament to the power of hope and determination, as Achel continues to inspire individuals facing their own battles with liver cancer through his experiences and insights.
Conclusion and the Future of Liver Cancer Research
In conclusion, liver cancer continues to pose significant challenges in both diagnosis and treatment. The insights shared throughout this blog post have highlighted the multifaceted nature of Achel Yaffe liver cancer, detailing its causes, symptoms, and current therapeutic strategies. Understanding the various risk factors, such as chronic hepatitis, alcohol consumption, and metabolic disorders, provides crucial context for both patients and healthcare providers. Furthermore, recognizing the symptoms associated with the disease is imperative for timely intervention, which can greatly influence outcomes.
Looking ahead, the current landscape of liver cancer research is vibrant and full of potential. Ongoing studies are seeking to better understand the biological mechanisms that drive liver cancer development, paving the way for innovative therapies. Researchers are focusing on targeted therapies aimed at specific molecular pathways, which may offer new hope for patients who do not respond to conventional treatments. Immunotherapy is another exciting area of exploration, showing promise in enhancing the body’s own defenses against cancer cells.
Additionally, the importance of funding and support for liver cancer initiatives cannot be overstated. Continued investment in research is essential to uncover new treatment modalities and improve survival rates. Advocacy plays a crucial role in raising awareness and ensuring that liver cancer receives the attention it deserves from the medical community and policymakers alike.
As we progress into the future, staying informed about advances in liver cancer research is vital. Patients and supporters are encouraged to engage with organizations dedicated to liver cancer awareness and research funding. By uniting efforts in education, advocacy, and support, we can work towards better outcomes for those affected by this disease and contribute to the overarching goal of finding a cure.

 16 October 2024
16 October 2024 Share
Share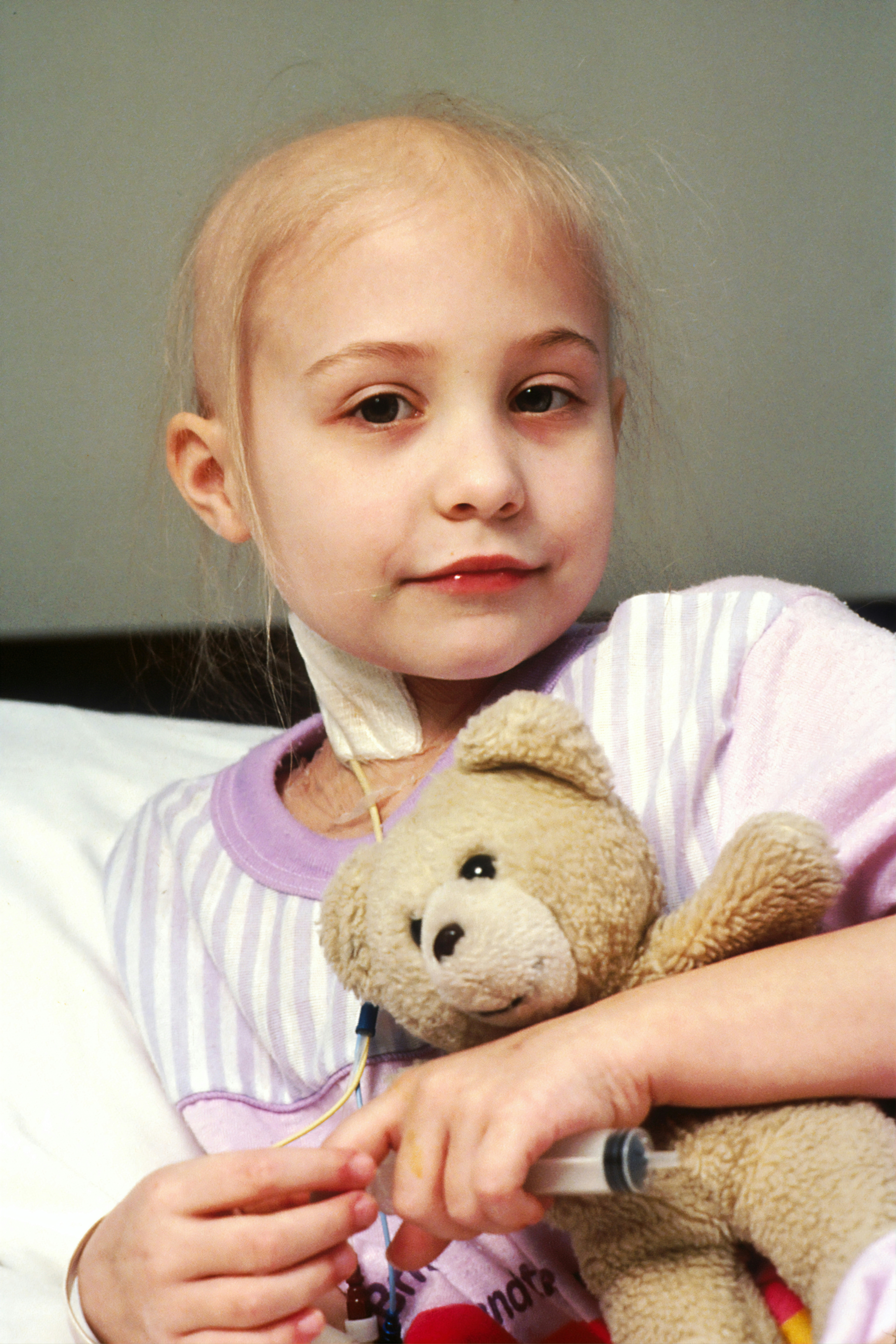
![Binance Dominates with $2.6B in Token Airdrops & Rewards [2025 Report]](https://hamstercombetworld.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Binance-Dominates-with-26B-in-Token-Airdrops-Rewards-2025.png)





